Understanding different internet connection types for your IP security cameras
The world of IP (internet protocol) cameras is as vast as security cameras themselves; from small, simple-setup devices to WiFi-connected hidden cameras to entire networks of professional-grade cameras linked up through an NVR (network video recorder), all of these cameras rely on a connection to the '
internet, and every connection requires an IP address. IP addresses are like postal addresses; defined locations assigned by an internet service provider (ISP) which dictates where data is delivered.
When you purchase an IP camera, the type of network may dictate how that camera will work for you. In this article we'll look at the different types of IP connections that exist, when and why they're used, in addition to some troubleshooting efforts you can make with your IP camera.
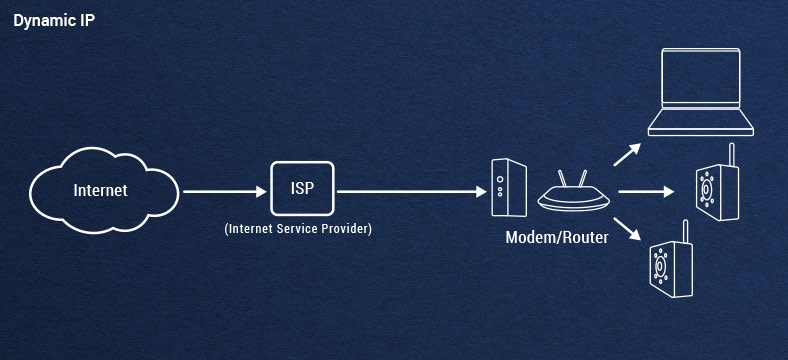
What Is A Dynamic IP Address?
As we stated previously, an IP address is a general address given to an internet-connected device (like a camera or a tablet) by the ISP. But, because there are billions of internet-connected devices in the world, and each device needs an IP address, not every device can be assigned one single address for its entire lifespan; the amount of addresses that ISPs would have to keep up with would be astronomical. As a result, dynamic IP addresses are designed to change constantly with each device.
Dynamic IP addresses are the most common consumer IP address type. While there is one set of IP addresses worldwide, oftentimes your home will be provided with a set of local IP addresses that your devices will use for a while, and then switch to a different address when the device is rebooted or after a certain period of time. Addresses are assigned by something known as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and always takes the form of eight numbers separated by three periods (1.334.34.20 for example).
Most consumers rely on dynamic IP addresses because they're not only the most cost-effective option, but they also provide the best out-of-the box security without the need for network administration. By avoiding network administration there is also minimal setup and maintenance cost, allowing an end user to be up and running on the internet almost immediately upon installation.
The downside to dynamic IP addresses is that, while they provide the best baseline security, oftentimes the end user is left with whatever protocols the ISP has. There is less room for customization, which can mean network vulnerabilities. Dynamic IPs also tend to have slower download and upload speeds because they're built for consumer-grade use, which typically demands less bandwidth of the network.
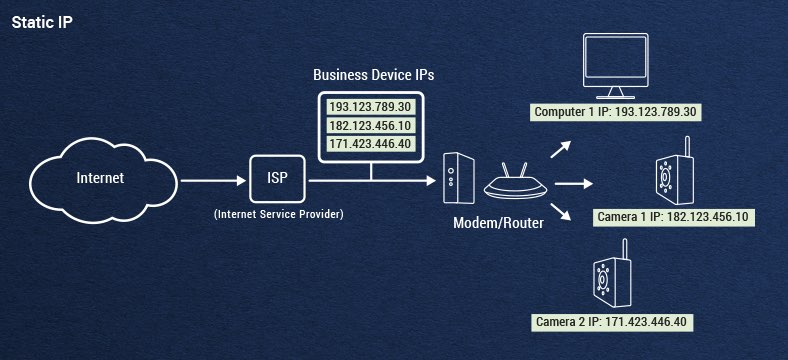
What Is A Static IP Address?
Conversely, a static IP is a permanently assigned address typically associated with commercial networks. When using a static IP address, each device must be assigned its address manually. Businesses usually rely on static IP addresses because it enables individual computers to maintain a steady network connection without swapping IP addresses upon reboot. This continuous network connection also enables a lot of the features businesses require of a stable connection: Voice over internet protocol (VOIP), over-the-air network updates, performance monitoring, etc.
While dynamic IP addresses are great for their ease of use, static IP addresses enable enhanced customizations critical to companies (websites especially) that host servers. Out-of-the-box dynamic IPs provide a solid baseline of security, but static IP addresses allow for professional-grade firewalls and additional security measures that are difficult to implement in a system where IP addresses are constantly shifting. The stability of connectivity also typically means that upload and download speeds are faster.
Static IP addresses are the more expensive option because by requisitioning a set of addresses you're taking them off the table for the ISP to use in the pool of dynamic IP addresses. Also, because the addresses are fixed, if a user winds up blocked from websites tracking IPs, that block may be permanent.
What Does This Mean To You?
At BrickHouse Security, we offer a wide array of IP cameras. Occasionally, when attempting to connect a camera to a network, a user may run into problems based on the IP address type. For example, when configuring a camera to your home network which features a dynamic IP, the camera will set up easily because your ISP will automatically recognize the camera and assign it an address. Then, if you were to bring that camera to your office, or if you're a retail loss professional bringing a camera to a business, the camera doesn't work; this could be because you're attempting to connect the device to a network with static IP addresses (and resulting enhanced firewalls).
While there is no clear-cut way to constantly have a connection with your camera across networks, there are some workarounds that can help establish connections on static IP networks, or create more secure connections on networks with higher vulnerabilities. One way to bypass static IP rigidity is through a process known as port forwarding. Port forwarding unlocks ports in a router or network that are usually closed off. While the process can be complicated, there are articles that can help assist in setting up a connection should you run into problems with an IP camera.
Another way to combat connection problems, specifically related to firewalls, is the use of a proxy server. A proxy server creates an alternate, intermediary internet connection for your device. By bypassing a direct internet connection, a device can avoid network-installed firewalls and other restrictions. Again, the process can be complicated, and there are a few ways of setting up proxy servers, but there are plenty of how-tos out there that can assist along the way.
As always, these network connection issues will come through on a case-by-case basis, and every problem will be specific to the user and device. Hopefully, this guide served as an introduction to how IP addressing and network connection works in order for you to have a baseline when troubleshooting your device. Our experts are also here to help walk you through any issues you may have. Just give us a call at (800) 654-7966.
Published March 14th, 2021
